How can one best prepare for a financially stable retirement? Thoroughly understanding the available retirement savings vehicles is essential. Among the most beneficial strategies for many investors is optimizing tax-free retirement options.
With these options, you can maximize potential returns by minimizing tax liabilities. While tax free retirement accounts represent one of the interesting paths in this realm, they are just one of the many options available to those aiming for tax-free income in their golden years.
In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the diverse tax-free retirement options for 2024, providing you with the insights needed to make informed decisions and strategically shape your retirement route.
Retirement Planning With Life Insurance
One way to generate tax-free income is achieved through options like the indexed universal life insurance policy, a variable life policy, or a whole life insurance policy. Governed by Section 7702 of the Internal Revenue Code, these insurance products aim to furnish tax-free income during one’s retirement years.
Financial professionals often promote these products to individuals keen on exploring alternative routes to save for retirement, setting them apart from traditional options like 401(k)s, pensions, or individual retirement accounts (IRAs).
Yet, it’s important to recognize that life insurance is not considered a retirement account in the true sense. They are, in fact, life insurance contracts with the primary purpose being the death benefit to the stated beneficiaries.
How does the cash value inside of a life insurance policy work?
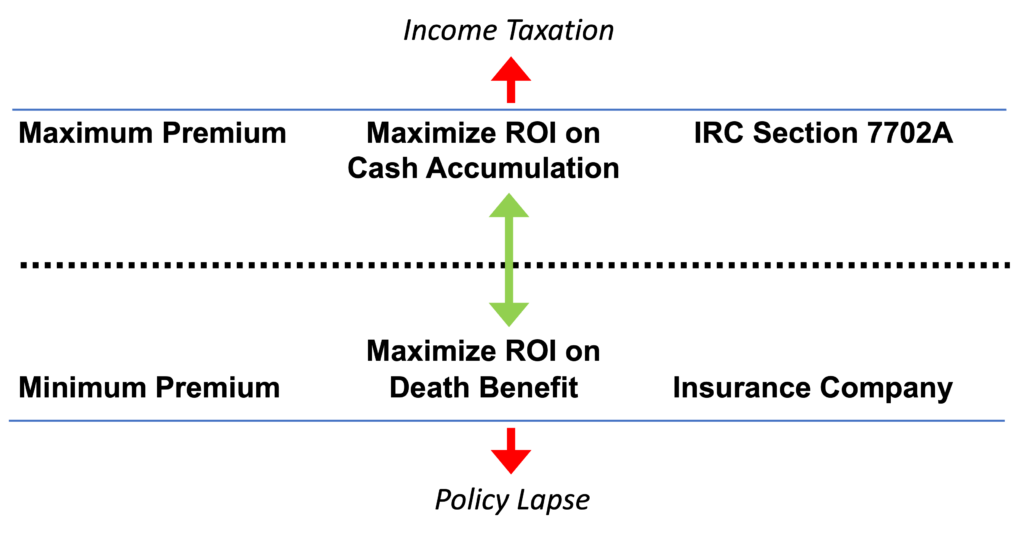
A permanent cash-value life insurance policy is funded through after-tax premium payments (contributions), much like contributions to a Roth IRA. Owners of a life insurance cash value policy have access to different payment options: (1) A minimum premium payment will keep the policy in-force (2) The planned (or target) premium is a suggested premium that indicates the amount of premium that should keep a given universal life policy in force in the coming years. (3) The maximum premium option uses Section 7702 of the IRS code to maximize the cash-value portion of the life insurance contract, which can ultimately build a large amount of tax-free cash value.
As the policy’s cash value grows, it does so on a tax-deferred basis, and policyholders can access this cash value through tax-free loans during their lifetime. Cash value accumulation within the policy can vary based on the chosen investment approach.
What sets life insurance contracts apart from retirement accounts is that they aren’t categorized as qualified plans, meaning they don’t adhere to the same rules and tax terms as such plans.
The cash value inside of a life insurance policy is not a qualified retirement plan. Therefore, the loan/withdrawal feature is not subject to the same penalties as those plans. Policyholders don’t have to worry about a 10% early withdrawal penalty if funds are extracted from the policy before reaching the age of 59 ½, unlike traditional 401(k)s or IRAs.
Key Benefits of Life Insurance
Cash-value inside of a life insurance policy offer unique advantages, distinct from traditional retirement savings avenues. Designed to optimize post-retirement income by minimizing tax liabilities, they present a compelling choice for forward-thinking individuals. Here are the primary benefits:
- Receive tax-free income in retirement.
- Distinct tax advantages.
- Stands out as a powerful tool for securing tax-free retirement income.
Other Common Tax-Free Retirement Options
Planning for retirement isn’t just about storing money; it’s about understanding the various tools available to maximize your savings and minimize your tax liabilities. Tax-free retirement options offer unique advantages that can help optimize your post-retirement income. Let’s explore some of these options:
1. Roth IRA

A Roth IRA is an individual retirement account where contributions are made with post-tax earnings. Unlike traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs don’t grant a tax break for contributions. However, their true advantage lies in the withdrawal phase.
Benefits
- Tax-free withdrawals after the age of 59½ and/or account is opened for more than 5 years
- No lifetime required minimum distributions
- Flexibility in investment options
- Tax-free inheritance
2. Roth 401(k) and Roth 403(b)

Employer-sponsored retirement accounts merge traditional 401(k) or 403(b) features with Roth IRA elements. The unique structure allows employees to contribute to retirement with after-tax dollars through their workplace.
Benefits
- Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, ensuring tax-free retirement income.
- Suitable for individuals who expect to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement.
- No lifetime required minimum distributions
Comparing with Traditional 401(k) and 403(b)
Roth accounts you pay tax now versus traditional retirement plans where you pay tax later on withdrawals.
3. Municipal Bonds

Municipal bonds, or “munis,” are debt securities issued by state and local governments. Investing in these bonds means you’re lending money to these governmental bodies. The primary appeal of municipal bonds lies in their tax treatment.
Benefits
- Tax-exempt interest income from these bonds is typically free from federal taxes.
- It can reduce taxable income, depending on the state of issuance and residence.
How They Work
By lending money to governmental entities, investors are compensated with interest, which often escapes the reach of the government.
4. Health Savings Account (HSA) for Retirement

Though HSAs are primarily designed to offer individuals a tax-advantaged way to pay for medical expenses, they come with a unique structure that can be tapped for retirement benefits.
Benefits
- Funds grow tax-free and can be withdrawn tax-free for qualified medical expenses.
- After age 65, funds can be withdrawn for any reason without penalty but are subject to ordinary income tax if not used for medical expenses.
- Contributions offer a tax deduction, reducing current taxable income.
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Tax-Free Retirement Option

Choosing a tax-free retirement option is crucial in one’s financial planning journey. While the allure of tax-free growth and withdrawals is strong, making informed choices is essential. Below are key factors you must consider:
1. Assessing your Current Tax Bracket and Future Projections
Your current tax bracket and where you anticipate being during retirement can influence which retirement option is best. If you foresee yourself moving into a higher tax bracket, options offering tax-free withdrawals can be more beneficial.
If you’re currently in a high bracket but anticipate a lower one post-retirement, the immediate tax deductions of some vehicles might be preferable.
2. Understanding Contribution Limits and Potential Penalties
Each tax-free retirement option, governed by the Internal Revenue Code, has stipulated contribution limits. It’s crucial to be aware of these limits to avoid over-contributing.
Overstepping these boundaries can result in unnecessary penalties. Some plans might have withdrawal conditions, and not adhering to these can result in penalties.
3. Analyzing Your Volatility Tolerance and Investment Strategy
Every individual has a unique appetite for volatility, directly impacting investment choices. For instance, someone with a higher volatility tolerance might lean towards equities within their Roth IRA, while another may choose bonds.
The versatility of some options, like a life insurance policy that can also serve as a tax-free retirement option due to its cash value feature, can appeal to those looking for dual benefits. Understanding how each option aligns with your overall investment strategy is important.
Importance of Diversifying Retirement Savings
Diversifying retirement savings resembles the adage: “Don’t put all your eggs in one basket.” This time-tested wisdom speaks to the core of financial security. Here’s why it’s crucial:
Mitigating Risk
By spreading investments across different vehicles, you reduce the potential damage if one of them underperforms. A singularly focused investment strategy can expose your savings to unnecessary vulnerabilities.
Balanced Approach
Incorporating a mix of tax-deferred, taxable, and tax-free accounts ensures you benefit from a multi-faceted savings strategy.
While tax-free accounts like Roth IRAs offer tax-free retirement income, taxable accounts can be flexible regarding withdrawals, and tax-deferred ones provide immediate tax deductions. Utilizing all three can optimize both savings and tax benefits.
Final Thoughts
The landscape of retirement planning is continually evolving, with an increasing emphasis on understanding and guiding tax implications.
Given the potential tax law changes, national debt and increasing financial pressures facing retirees today, leveraging tax-free retirement options like the tax-free retirement account is not just a luxury—it’s an imperative.
From Roth IRAs to innovative mechanisms like the cash value inside of a life insurance policy, these tax-advantaged avenues can play a significant role in helping you generate tax-free income. But remember, while these options offer promising benefits, their complex details and nuances demand a deep understanding.
Having professional guidance can be invaluable. If you’re keen to explore these tax-free retirement options further or need personalized financial advice tailored to your situation, we’re here to help.
Request a Getting to Know You Meeting, and let’s chart a course for your secure, tax-advantaged future.

